What is the Difference between a COVID-19 Viral or Antibody Test?
The Bottom Line
- The Viral Molecular (PCR) is the test of choice because it is the most accurate way to determine if you have an ACTIVE infection.
- We do not recommend an Viral Antigen test since it is less accurate than the Molecular (PCR) test.
- We do not recommend an Antibody Test since it will only tell you if you have had a PRIOR infection and cannot tell you whether you are immune to COVID-19.
- Ask your Testing Site if they provide a Viral Molecular (PCR) test and how long results take (should be no longer than a few days)
- Click here and search by your Zip Code to find a testing location.
Why a Pharmacy is a Great Place for COVID-19 Testing
Due to the surge of new COVID-19 cases, testing has become more important than ever. Fortunately, pharmacists are now authorized in every state to order and administer COVID-19 antibody and viral tests. Local pharmacies are one of the most convenient locations to complete a COVID-19 antibody or viral test. The reason being is that pharmacies are easily accessible to the public to provide quick and accurate testing for patients. Contact your local pharmacy to see if they provide COVID-19 testing. The purpose of this article is to help you become familiar with and understand the differences between the several types of COVID-19 tests.
The two available COVID-19 tests are viral tests and antibody tests. In short, a viral test will tell you if you have a CURRENT infection, whereas an antibody test will tell you if you have had a PAST infection. Before we discuss the differences between the COVID-19 viral and antibody tests, let’s first go over who should be tested for COVID-19 infection.
Who should be tested for COVID-19 infection?
You should be tested for COVID-19 if you have symptoms and have been in contact with someone with known or suspected COVID-19. The most common symptoms are fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Other symptoms include chills, muscle pain, new loss of taste or smell, vomiting or diarrhea, and/or sore throat. The highest priority for testing should go to symptomatic people who are healthcare workers, first responders, hospitalized patients, the elderly, or people who live in nursing homes, long-term care facilities, prisons, or shelters.
Now let’s discuss the differences between COVID-19 viral and antibody tests in greater detail below.
The Two COVID-19 Viral Tests You Should Know About
A COVID-19 viral test will tell you if you have an ACTIVE infection with COVID-19. Pharmacies which provide COVID-19 viral tests will collect samples from either outside the pharmacy or with a drive-thru service. The collected samples are then sent to a lab that will test and analyze the results. I recommend you ask the testing site how long it will take to get your results. The results should take a few days at most. At any rate, the viral test uses a long Q-tip-like nasal swab to collect a respiratory sample as you can see in the picture below.
There are two types of viral tests: Molecular (or PCR) tests or Antigen tests. Molecular tests will detect a genetic molecule called RNA from the COVID-19 virus. Antigen tests detect bits of viral protein from the COVID-19 virus. It is important to know which type of COVID-19 viral test you are getting since the Molecular (or PCR) test is more accurate than the Antigen test. The Molecular test is right about 95% of the time if your results come out negative for COVID-19, and 100% right if your results come out positive for COVID-19. The Antigen test, however, is only right about 80% of the time if your results are negative for COVID-19. So, if you get an Antigen test and the results are negative but you still have symptoms, the results may be wrong.
There are many reasons why a COVID-19 test results may be negative even though you have been infected with the COVID-19 virus. False negatives can happen if the swab did not go deep enough into your nose and throat to get a good sample or if your infection is too new. Sometimes COVID-19 tests will give negative results if you test for it too early after exposure. For this reason, when you visit countries like South Korea, you may be quarantined for 14 days even though your COVID-19 test result comes out negative, and retested again after the 14 days to see if the results have changed.
We recommend you should get a Molecular (or PCR) test done instead of an Antigen test. The Antigen test may be quick and cheap, but it is only correct 80% of the time if your results come out negative for COVID-19. You can still get an Antigen test if a Molecular test is not available since an Antigen test is better than nothing to test for COVID-19. But if you test negative for COVID-19 with an Antigen test and still have symptoms such as a fever and cough, you may want to consider getting a Molecular test to confirm you are truly negative for COVID-19.
Why You Don’t need a COVID-19 Antibody Test
The second type of COVID-19 test is the Antibody test. Antibodies are proteins that your immune system makes to fight off infections. Unlike the Viral test for COVID-19, the Antibody test does not test for ACTIVE infections. Rather, the Antibody test only detects a PRIOR infection. It can take a few weeks for your body to develop antibodies to an infection. An Antibody test uses a blood sample from a finger-stick prick or a needle puncture through your arm vein, rather than a nasal swab, so you do not have to worry about having a long Q-tip being stuck down your nose.
The Antibody test results are about 95% accurate if you are positive for a PRIOR COVID-19 infection. Unfortunately, a positive result does not mean you are immune to COVID-19 or have enough antibodies to prevent a reinfection. The reason why nobody knows if a person is immune to COVID-19 is that the COVID-19 virus is simply too new and has not infected enough people. Therefore a positive Antibody test does not mean you are safe from getting re-infected with COVID-19 again. Plus there is a 5% chance your positive Antibody results are wrong.
On the other hand, the Antibody test results are about 90% accurate if you are negative for a PRIOR COVID-19 infection. A negative results means you probably have never had COVID-19.
The Verdict: Viral vs. Antibody Tests
So should I get a COVID-19 Viral or Antibody test? I recommend getting a COVID-19 Viral test if you have symptoms or feel you have been exposed to the virus. The Viral test will help you determine if you have an ACTIVE infection. This information is vital so that you know how you can best be treated and whether you need to quarantine yourself from friends and family. If you get a Viral Test, make sure to get the Molecular (PCR) test, not the Antigen test, since the Molecular test is more accurate than the Antigen test.
I do not recommend getting the Antibody test, however, because it will only tell you if you have had a PRIOR infection, but it does not tell you if you have an ACTIVE infection. Knowing whether you have had a PRIOR infection has very limited value since it is too early to say whether a positive test means you are immune to COVID-19. We simply do not have enough data to determine whether you can be re-infected with COVID-19 even though you may have developed antibodies to this virus.
Where to get tested for current COVID-19 infection
Your local health department can tell you where you can get a COVID-19 test. Click here to be directed to a Directory of Local Health Departments. You can then search by your Zip Code for your local health department.
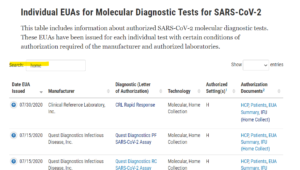
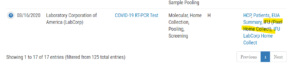
You can also get tested at home with an at-home molecular (PCR) COVID-19 test. Click here for a list of Labs that provide at-home test kits. Scroll to the bottom of the page and search by “home” for a list of Labs (see image below)
Then click where it says IFU (instructions for use) to find the website of the Lab providing the at-home COVID-19 test kit.
In this example, clicking the “IFU (Pixel Home Collect)” link will open up a PDF which has a clickable link to the www.pixel.labcorp.com website where you can order your testing kit (see image below).
Please note, some at-home COVID-19 testing kits are actually covered by your health insurance or may require a prescription from your doctor.
For more information:
The White House has created a quick fact sheet entitled “Guidance on Interpreting COVID-19 Test Results.” Click here for that document to help you understand how to interpret results from a COVID-19 antibody or viral test.
For more information on Testing for COVID-19, click here for a nice summary from the CDC for understanding the difference between a COVID-19 antibody or viral test.
And as always, please consult your doctor first to determine if you should get tested for COVID-19.